Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that is caused by the overproduction of melanin, which is the pigment that gives your skin its color. While melanoma is not contagious, it is one of the most serious types of skin cancer.
This skin condition can quickly spread to other parts of your body if left untreated. This article will discuss the causes of melanoma, how fast it can grow, as well as the symptoms and treatment options for this deadly disease.
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a type of cancer that begins in melanocytes, the cells that produce the pigment melanin. This type of cancer is relatively rare, accounting for only 1% of all cases of cancer. However, melanoma is one of the most serious types of skin cancer. It can quickly spread to other parts of your body if left untreated.
Types of Melanoma
Cutaneous (Skin) Melanoma
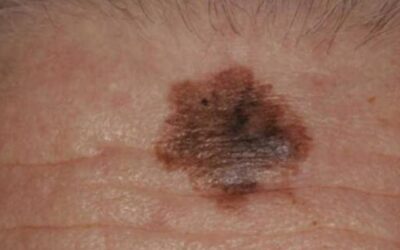
The most common type of melanoma, cutaneous melanoma begins in the skin cells. This type of melanoma is usually identified by the appearance of black, brown, or tan spots on the skin.
Ocular (Eye) Melanoma
Ocular melanoma is the most serious form of melanoma, and is responsible for the majority of melanoma-related deaths. This type of melanoma begins in the cells of the eye, and can quickly spread to other parts of the body.
Mucosal Melanoma
Mucosal melanoma is a rare form of melanoma that begins in the mucous membranes, such as the lips, mouth, or nose. This type of melanoma is often diagnosed at a later stage. It is associated with a higher rate of mortality than other forms of melanoma.
Causes of Melanoma
Melanoma is not contagious and is caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or other sources, such as tanning beds. Melanoma can also develop from moles (skin lesions that are usually brown or black).
This type of cancer is also common to those who have an inherited tendency to develop melanoma and certain skin conditions.
Symptoms of Melanoma
It is important to be aware of the early warning signs of melanoma, as it can often grow and spread rapidly if left untreated.
The most common symptoms of melanoma include:
- a new mole or growth on your skin that is dark, different from the other moles on your body, or is growing rapidly
- a change in the size, shape, or color of an existing mole
- itching, bleeding, or crusting of a mole
- pain or swelling in a lymph node
- any new symptoms, such as a lump or mass on your skin, fatigue, fever, night sweats, or changes in your bowel or bladder habits.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor right away.
Risk of Melanoma
Anyone can develop melanoma, but people with fair skin, freckles, and light hair are at higher risk. This type of cancer is also more common in men than women.
The risk of melanoma increases with age and is highest among those over the age of 60.
People who have a family history of melanoma, or who have certain skin conditions, are also at increased risk for developing this deadly disease.
Diagnosis of Melanoma
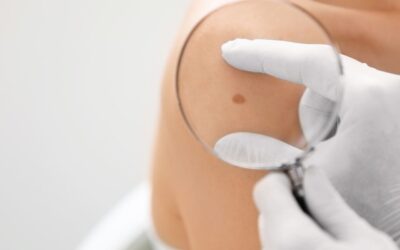
Melanoma is often diagnosed by the appearance of spots on the skin. These melanoma spots can be black, brown, or tan, and are often different from the other moles on your body. If you experience any changes in the appearance of your moles, it is important to see a doctor right away.
Medically, this condition is diagnosed through a biopsy, which is a procedure in which a sample of the tumor is removed for examination. This type of cancer can also be diagnosed with a blood test or imaging tests, such as a CT scan or MRI.
Further Melanoma Tests
If melanoma is diagnosed, your doctor will likely order additional tests such as a PET scan or a bone scan to determine the extent of cancer. Additional tests are also necessary to identify whether it has spread to other parts of your body. This is important for planning treatment.
How Fast Does Melanoma Spread?
Melanomas can grow quickly, and early detection is important for successful treatment. The five-year survival rate for people with melanoma is about 99% if the cancer is detected early. But it drops to about 15% if cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Melanoma Mole Treatment
The treatment of melanoma depends on the stage of the disease. If early melanoma symptoms are detected, it is often treated with surgery to remove the tumor. In some cases, radiation therapy or chemotherapy may also be used.
If melanoma has spread to other parts of the body, chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be used to slow the progression of the disease.
Can Melanoma Come Back?
Yes, melanoma can often come back after treatment. This is why it is important to have regular follow-up exams with your doctor, even after your cancer is treated.
How to Prevent Melanoma?
The best way to reduce your risk of developing melanoma is to protect your skin from the sun’s ultraviolet radiation. This can be done by using sunscreen, wearing a hat and sunglasses, and avoiding exposure to the sun during peak hours.
People with fair skin should also avoid tanning beds, as they are a major source of UV radiation.
It is also important to check your skin regularly for any changes. See a melanoma specialist if you notice anything unusual.
Visit Skin Cancer Dermatologists in Texas
If you are looking for more information on melanoma or would like to consult with a skin cancer specialist, please contact us at Skin Cancer Dermatologists in Texas. We offer a wide range of services to help you treat this deadly disease.
Skin Cancer Dermatologists is a specialized medical practice that is dedicated to the diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer.
Our team of experienced dermatologists offers a wide range of services to help patients fight melanoma and other skin cancers. We offer a range of treatments, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. We also offer comprehensive follow-up care to help ensure the best possible outcome.
Key Takeaways
In conclusion, melanoma is deadly cancer that can often grow and spread rapidly if left untreated. However, early detection is important for successful treatment.
There are many ways to reduce your risk of developing melanoma. That includes using sunscreen, wearing a hat and sunglasses and avoiding exposure to the sun during peak hours. It is also important to check your skin regularly for any changes and to see a doctor if you notice anything unusual.