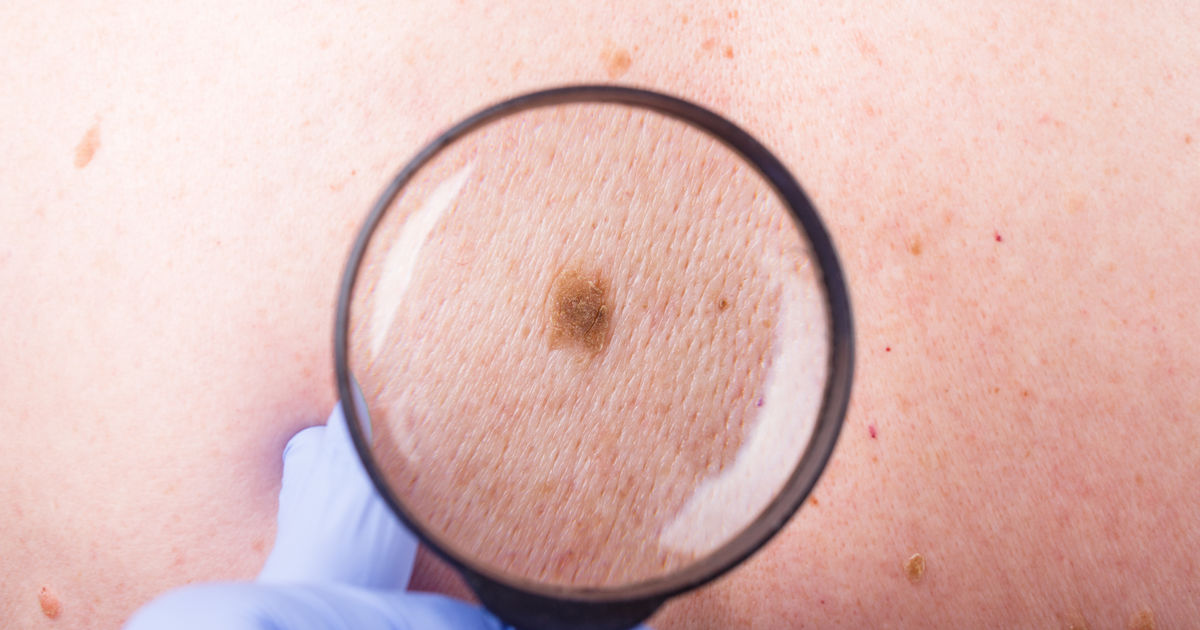
Melanoma is one of the most serious types of skin cancer, but the good news is that it’s highly treatable when detected early. Whether you’re concerned about a suspicious mole or simply want to stay informed, this guide will walk you through what melanoma is, how to recognize it, and the best ways to protect yourself.
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops from melanocytes—the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. While it’s less common than other forms of skin cancer, such as basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma is much more aggressive and can spread to other parts of the body if not treated early.
What Causes Melanoma?
Melanoma is primarily caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds, which damages skin cell DNA. However, genetics also play a role. If you have a family history of melanoma, your risk may be higher.
Who is at Risk?
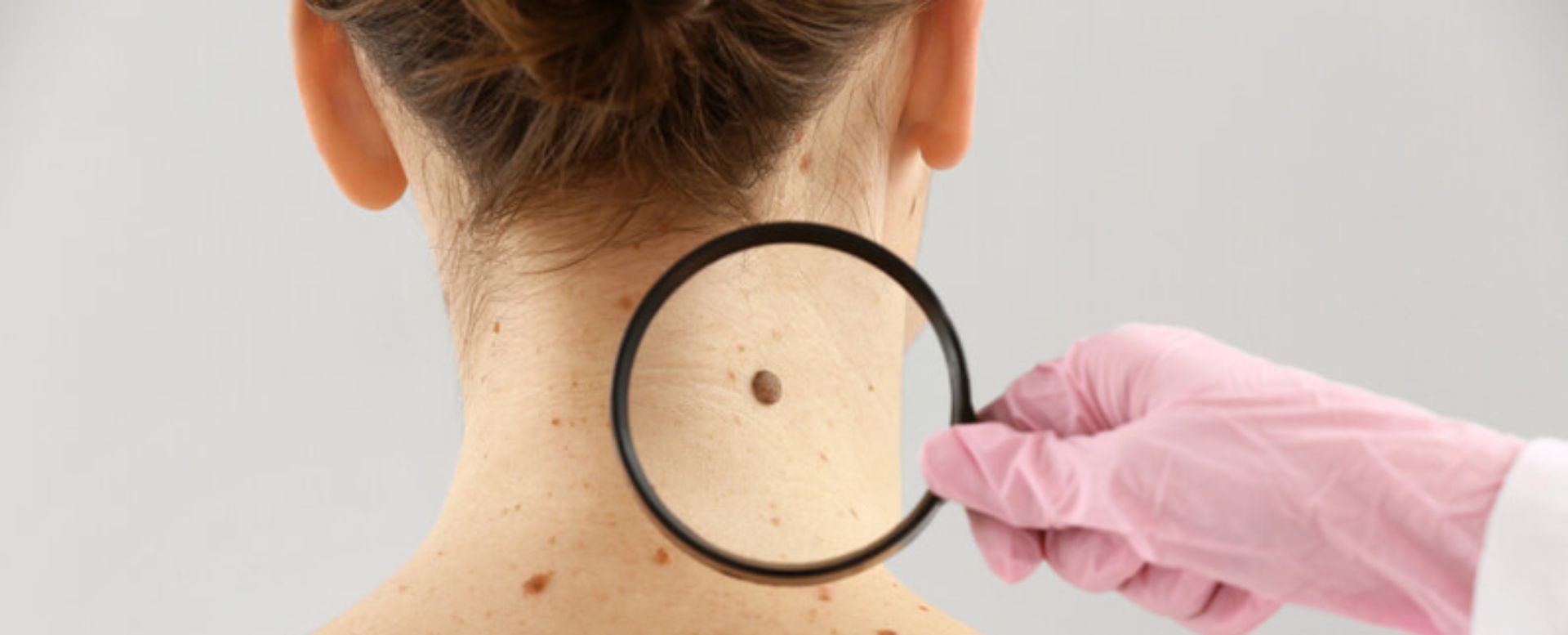
Anyone can develop melanoma, but certain factors increase the risk, including:
- Excessive UV exposure (sunburns, tanning beds, or prolonged sun exposure)
- Fair skin, light hair, and light eyes (less melanin means less natural protection)
- Family history of melanoma
- A high number of moles or atypical moles
- Weakened immune system
- Age (risk increases with age, but younger people can also develop melanoma)
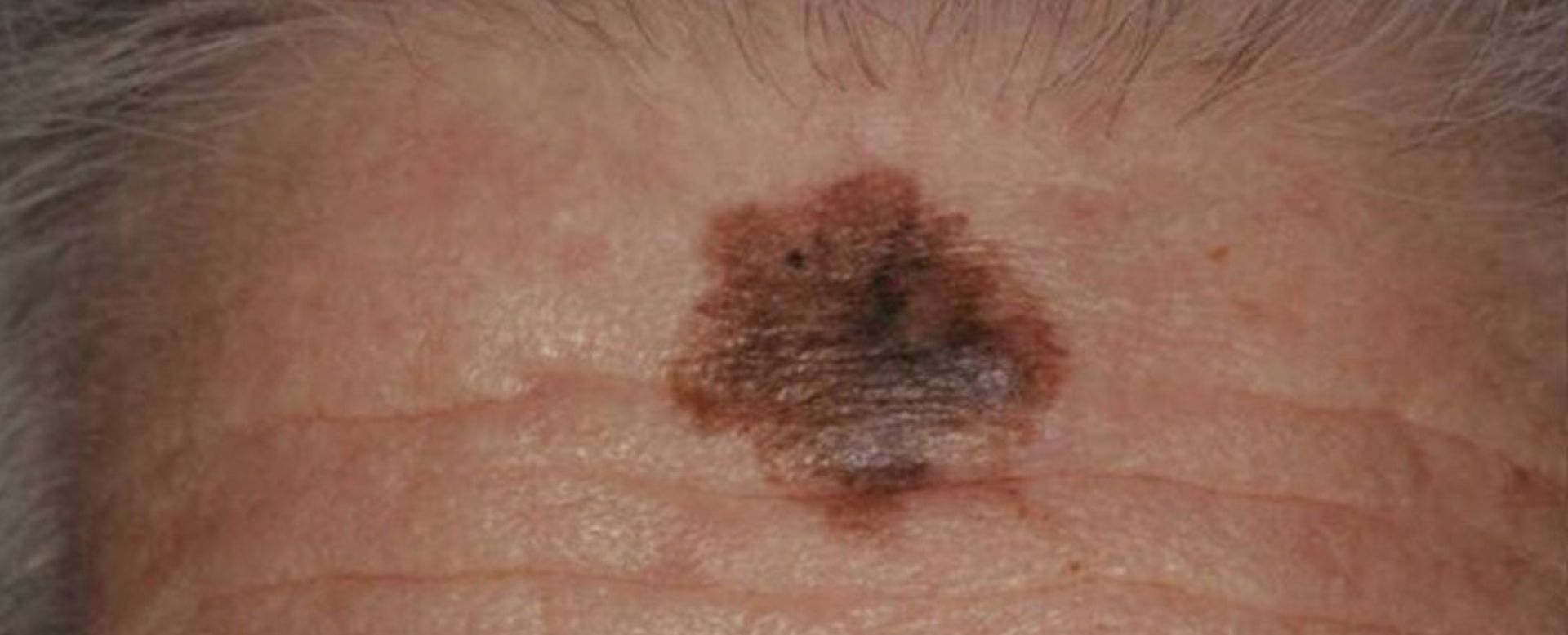
How to Identify Melanoma: The ABCDE Rule
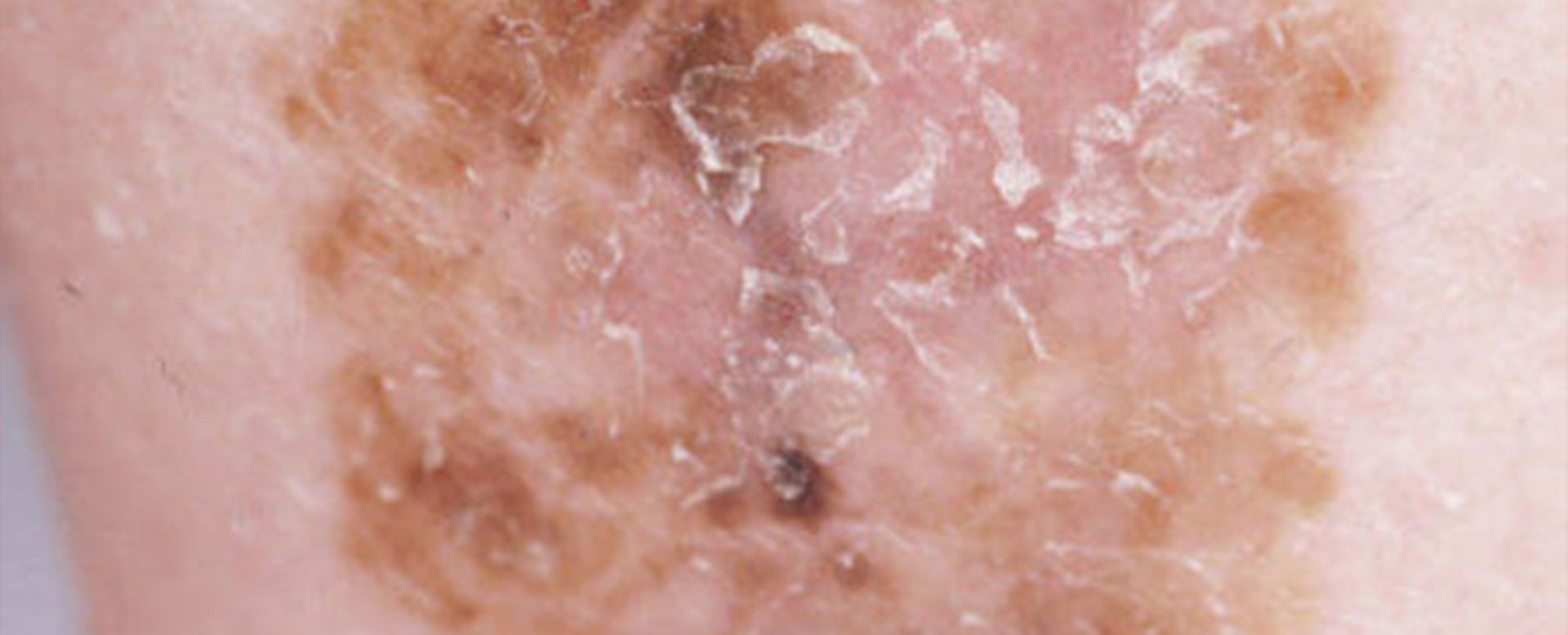
Early detection is crucial for successful treatment. Keep an eye on moles and skin changes using the ABCDE rule:
- A – Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn’t match the other.
- B – Border: Irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined edges.
- C – Color: Multiple colors (brown, black, red, white, or blue) within the same spot.
- D – Diameter: Larger than a pencil eraser (about 6mm), though melanomas can be smaller.
- E – Evolving: Any change in size, shape, color, or symptoms (itching, bleeding, etc.).
If you notice any of these warning signs, schedule an appointment with a dermatologist immediately.
How is Melanoma Diagnosed?
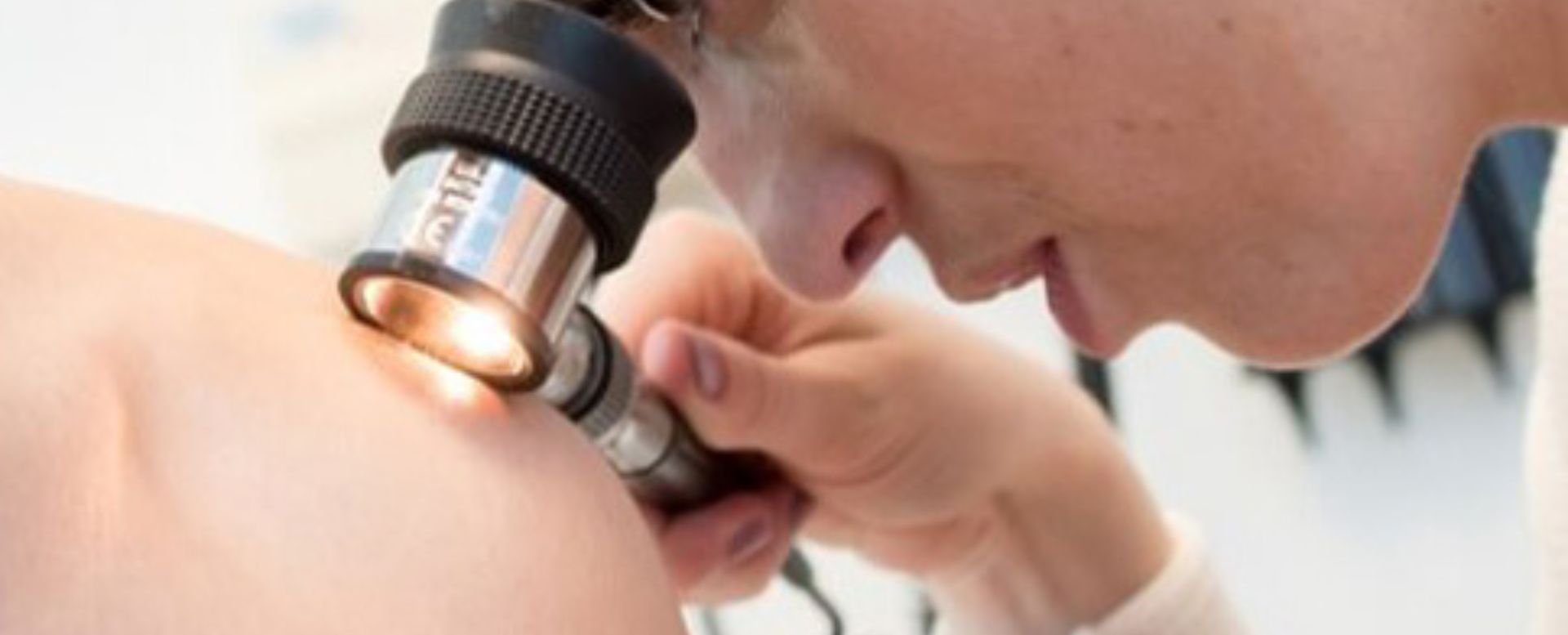
A dermatologist will examine the suspicious spot and may perform a biopsy, where a small sample of skin is taken and analyzed under a microscope. If melanoma is confirmed, additional tests may be needed to determine whether it has spread.
Treatment Options for Melanoma

The best treatment depends on the stage of melanoma. Common options include:
- Mohs Surgery: A precise technique that removes cancer layer by layer while preserving healthy skin.
- Wide Excision Surgery: Removes the melanoma along with a margin of healthy skin.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Uses drugs designed to attack specific genetic mutations in melanoma cells.
- Radiation Therapy & Chemotherapy: Used in advanced cases to target cancer cells.
Prevention: Protecting Your Skin
Preventing melanoma is easier than treating it. Follow these skin-saving tips:
- Wear sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) every day, even on cloudy days.
- Avoid tanning beds as they significantly increase melanoma risk.
- Seek shade during peak sun hours (10 AM – 4 PM).
- Wear protective clothing, including wide-brim hats and sunglasses.
- Perform monthly skin checks and visit a dermatologist annually.
When to See a Dermatologist
If you notice any suspicious moles, experience persistent skin changes, or have a family history of melanoma, don’t wait. Book a skin cancer screening today. Early detection could save your life.
Melanoma may sound scary, but knowledge is power. By staying informed and taking preventive steps, you can greatly reduce your risk. If you have concerns, reach out to a trusted dermatologist near you.
Need an Expert Opinion?
Skin Cancer Specialists offers top-tier melanoma screenings and treatments in Sugar Land, Conroe, Katy, and Memorial, Texas. Book your appointment today and take control of your skin health!